Maharashtra Board 10th Class Maths Part 1 Practice Set 1.3 Solutions Chapter 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables
Practice Set 1.3 Algebra 10th Std Maths Part 1 Answers Chapter 1 Linear Equations in Two Variables
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks with correct number.
Solution:
Question 2.
Find the values of following determinants.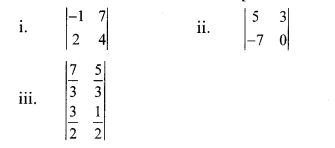
Solution: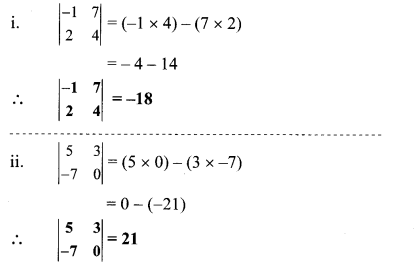

Question 3.
Solve the following simultaneous equations using Cramer’s rule.
i. 3x – 4y = 10 ; 4x + 3y = 5
ii. 4x + 3y – 4 = 0 ; 6x = 8 – 5y
iii. x + 2y = -1 ; 2x – 3y = 12
iv. 6x – 4y = -12 ; 8x – 3y = -2
v. 4m + 6n = 54 ; 3m + 2n = 28
vi. 2x + 3y = 2 ; x –
Solution:
i. The given simultaneous equations are 3x – 4y = 10 …(i)
4x + 3y = 5 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 3, b1 = -4, c1 = 10 and
a2 = 4, b2 = 3, c2 = 5
∴ (x, y) = (2, -1) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
ii. The given simultaneous equations are
4x + 3y – 4 = 0
∴ 4x + 3y = 4 …(i)
6x = 8 – 5y
∴ 6x + 5y = 8 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 4, b1 = 3, c1 = 4 and
a2 = 6, b2 = 5, c2 = 8
∴ (x, y) = (-2, 4) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
iii. The given simultaneous equations are
x + 2y = -1 …(i)
2x – 3y = 12 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = C1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 1, b1 = 2, c1 = -1 and
a2 = 2, b2 = -3, c2 = 12
∴ (x, y) = (3, -2) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
iv. The given simultaneous equations are
6x – 4y = -12
∴ 3x – 2y = -6 …(i) [Dividing both sides by 2]
8x – 3y = -2 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 3, b1 = -2, c1 = -6 and
a2 = 8, b2 = -3, c2 = -2
∴ (x, y) = (2, 6) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
v. The given simultaneous equations are
4m + 6n = 54
2m + 3n = 27 …(i) [Dividing both sides by 2]
3m + 2n = 28 …(ii)
Equations (i) and (ii) are in am + bn = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1m + b1n = c1 and a2m + b2n = c2, we get
a1 = 2, b1 = 3, c1 = 27 and
a2 = 3, b2 = 2, c2 = 28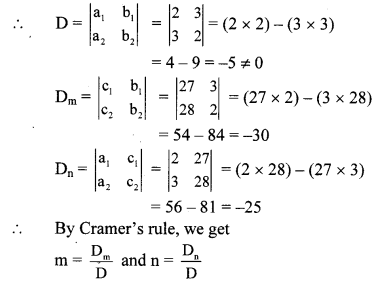

∴ (m, n) = (6, 5) is the solution of the given simultaneous equations.
vi. The given simultaneous equations are
2x + 3y = 2 …(i)
x =
∴ 2x – y = 1 …(ii) [Multiplying both sides by 2]
Equations (i) and (ii) are in ax + by = c form.
Comparing the given equations with
a1x + b1y = c1 and a2x + b2y = c2, we get
a1 = 2, b1 = 3, c1 = 2 and
a2 = 2, b2 = -1, c2 = 1
Question 1.
To solve the simultaneous equations by determinant method, fill in the blanks,
y + 2x – 19 = 0; 2x – 3y + 3 = 0 (Textbookpg.no. 14)
Solution:
Write the given equations in the form
ax + by = c.
2x + y = 19
2x – 3y = -3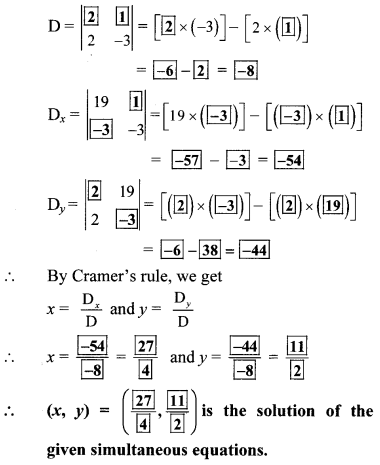
Question 2.
Complete the following activity. (Textbook pg. no. 15)
Solution:
Question 3.
What is the nature of solution if D = 0? (Textbook pg. no. 16)
Solution:
If D = 0, i.e. a1b2 – b1a2 = 0, then the two simultaneous equations do not have a unique solution.
Examples:
i. 2x – 4y = 8 and x – 2y = 4
Here, a1b2 – b1a2 = (2)(-2) – (-4) (1)
= -4 + 4 = 0
Graphically, we can check that these two lines coincide and hence will have infinite solutions.
ii. 2x – y = -1 and 2x – y = -4
Here, a1 b2 – b1 a2 = (2)(-1) – (-1) (2)
= -2 + 2 = 0
Graphically, we can check that these two lines are parallel and hence they do not have a solution.
Question 4.
What can you say about lines if common solution is not possible? (Textbook pg. no. 16)
Answer:
If the common solution is not possible, then the lines will either coincide or will be parallel to each other.
Comments
Post a Comment
write your query and get answer in 24 hours